In February 2026, Google released a significant core update that heavily impacted visibility in Google Discover. While core updates are common, this one stood out because of how strongly it affected content performance in the Discover feed.
Many publishers experienced sudden traffic shifts. Some saw dramatic gains. Others saw steep declines. In most cases, traditional search rankings remained relatively stable while Discover visibility changed rapidly.
If your site relies on mobile traffic, trending content, or editorial publishing, understanding this update is essential. In this guide, we will explain what changed, why Discover traffic is different from search traffic, what signals appear to have been strengthened, and how to adapt your strategy in a sustainable way.
The goal is not to react emotionally to traffic swings. The goal is to understand how Discover works and how to build content that performs consistently over time.
Understanding Google Discover

Google Discover is a personalized content feed that appears in the Google app and on many Android devices. Unlike traditional search results, users do not type a query. Instead, Google predicts what users may find interesting based on past behavior, interests, location, and engagement signals.
Discover is interest driven rather than query driven.
This distinction is critical.
Search traffic depends on ranking for keywords. Discover traffic depends on Google confidence that a user will engage with your content.
Discover content often includes:
- News and current events
- Industry updates
- Opinion pieces
- Evergreen guides with strong engagement
- Visually compelling content
Because Discover is predictive, traffic patterns are less stable. Content can generate large spikes and then disappear from the feed within days.
The February 2026 update appears to have refined how Google evaluates which content deserves that exposure.
What Is A Core Update
A core update is a broad adjustment to Google ranking systems. These updates are not penalties. They are reassessments.
Google continuously improves how it evaluates:
- Relevance
- Helpfulness
- Authority
- User satisfaction
- Trustworthiness
When a core update rolls out, Google recalibrates its systems. Some content may be reevaluated as more helpful. Other content may be reevaluated as less valuable.
In the case of February 2026, the recalibration had a visible impact on Discover distribution.
Websites that relied heavily on trend based publishing or viral headlines noticed stronger volatility than those focused on deep expertise and consistent topical authority.
What Changed In February 2026
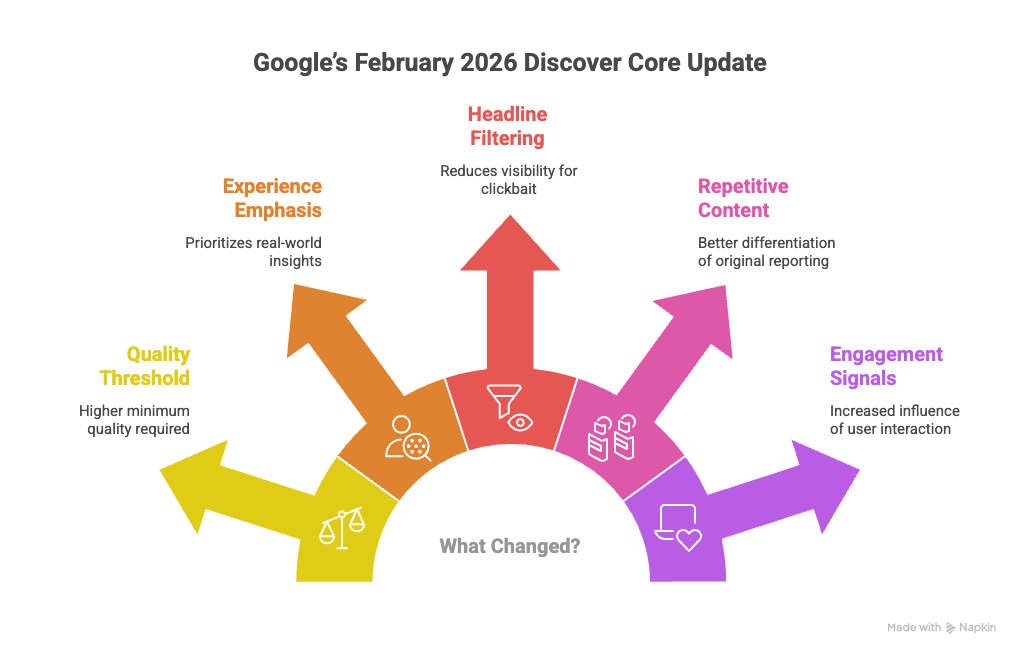
While Google does not publish detailed technical specifics for each update, data patterns and industry analysis suggest several strengthened signals within Discover.
1. Higher Quality Threshold For Inclusion
The update appears to have raised the minimum quality threshold required for Discover placement.
Content that was average but engaging may have previously qualified. After the update, only content that demonstrated clear value and strong engagement metrics continued to receive exposure.
2. Stronger Emphasis On Experience
Google continues to prioritize content created from real experience. Articles that demonstrated practical knowledge, case examples, or firsthand insight performed better.
Generic summaries that rephrased existing material without adding perspective saw declines.
3. Reduced Visibility For Click Driven Headlines
Discover is visually oriented. Strong headlines matter. However, misleading or exaggerated headlines now appear to be filtered more aggressively.
If the content did not satisfy the promise of the title, Discover visibility dropped quickly.
4. Improved Detection Of Repetitive Content
Trend based publishers often cover similar topics simultaneously. The February update appears to better differentiate between original reporting and repetitive commentary.
Original angles and deeper analysis performed better than surface level coverage.
5. Engagement Signals Gained Importance
Post click engagement appears to have become more influential.
Metrics likely evaluated include:
- Time on page
- Scroll behavior
- Return to feed rate
- Content interaction
Content that users abandoned quickly may have been deprioritized in future Discover cycles.
Why Discover Traffic Is Naturally Volatile
Discover traffic behaves differently from search traffic.
Search is intent based. A user types a query. Rankings remain relatively stable if your position remains stable.
Discover is predictive. Google decides what to show. Visibility depends on performance signals and algorithmic confidence.
This creates natural volatility.
Content may:
- Appear prominently for three days
- Generate significant traffic
- Then disappear completely
The February 2026 update amplified this volatility for lower quality content while stabilizing performance for higher authority sites.
Understanding this distinction prevents overreaction. Traffic swings in Discover do not always indicate technical problems. They often reflect recalibrated quality thresholds.
Who Was Most Affected
Based on performance trends across industries, the update significantly affected:
- News aggregators
- Affiliate heavy publishers
- AI scaled content sites
- Viral trend driven blogs
- Websites lacking clear author credibility
Sites that depended on volume rather than depth experienced sharper declines.
In contrast, brands with established authority and strong editorial standards saw more consistent Discover visibility.
Authority is not built overnight. It develops through topical depth, structured content planning, and high quality link signals. Many publishers that focus on advanced link building techniques within a clear editorial framework tend to experience greater resilience during core updates.
Signs Your Site Was Impacted
To determine whether your site was affected:
- Review the Discover report in Google Search Console
- Compare traffic before and after February 2026
- Look for sudden impression declines
- Analyze which content categories lost exposure
If traditional keyword rankings remained steady while Discover impressions dropped, the impact is likely related to this update.
It is important to separate Discover performance from search ranking performance. They are influenced by overlapping but distinct signals.
Content Patterns That Lost Visibility
Analyzing impacted sites reveals recurring patterns.
Thin Trend Coverage
Quick reactions to trending topics without depth were deprioritized.
Rewritten Industry News
Publishing similar summaries to dozens of other sites without original insight reduced uniqueness.
Over Reliance On Automation
AI tools can assist with drafting. However, publishing large volumes of lightly edited AI content without subject matter expertise appears to have triggered reduced exposure.
Weak Author Signals
Content without clear authorship, credentials, or editorial transparency struggled more in Discover.
Trust plays a large role in feed based content distribution.
Content Characteristics That Gained Visibility
On the other hand, several content characteristics performed well.
Deep Topical Authority
Websites that demonstrated subject mastery through interconnected content clusters saw improved stability.
This approach resembles structured programmatic SEO models where content expansion is strategic rather than random.
Clear Experience Signals
Articles that reflected real world expertise stood out. Including practical examples, step by step processes, or firsthand insights increased engagement.
Strong Visual Presentation
Discover is visually driven. High quality images with clear relevance to the topic improved click through rates.
Low quality stock photos reduced performance.
Consistent Publishing Standards
Brands with predictable editorial quality experienced less volatility.
Consistency builds algorithmic trust.
Recovery Strategy After February 2026 Update
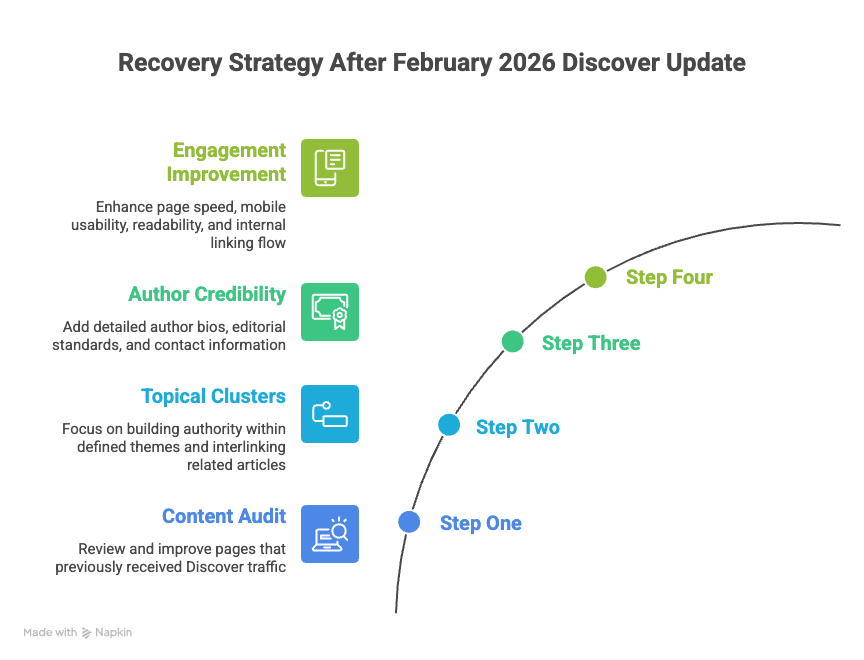
If your Discover traffic declined, recovery requires structured evaluation.
Step One Conduct A Content Audit
Review pages that previously received Discover traffic.
Evaluate:
- Depth of coverage
- Original perspective
- Engagement quality
- Visual strength
- Clarity of writing
Remove or improve content that does not provide substantial value.
Step Two Strengthen Topical Clusters
Instead of covering unrelated trending subjects, focus on building authority within defined themes.
Interlink related articles naturally. Create comprehensive guides that serve as cornerstone resources.
For example, when discussing content visibility, integrating insights about technical SEO for single page websites helps strengthen contextual relevance.
Step Three Improve Author Credibility
Add:
- Detailed author bios
- Clear editorial standards
- Transparent contact information
- Updated about pages
Trust indicators support Discover inclusion.
Step Four Improve Engagement
Enhance:
- Page speed
- Mobile usability
- Readability
- Internal linking flow
Short paragraphs, clear language, and logical formatting improve user satisfaction metrics.
Long Term Discover Optimization Principles
Discover is not a shortcut channel. It rewards quality.
Here are sustainable principles for long term performance.
Prioritize User Value Over Volume
Publishing fewer high quality articles is often more effective than producing large volumes of average content.
Blend Evergreen And Timely Content
Trend based articles can attract attention. Evergreen resources build authority. A balanced mix supports stability.
Focus On Clear Writing
Readable content increases engagement. Avoid complex sentences when simple ones communicate better.
Build Brand Recognition
Brand searches, consistent messaging, and high quality backlinks contribute to algorithmic trust.
Monitor Performance Regularly
Weekly review of Discover data allows early detection of shifts.
The Role Of Technical Foundations
While Discover emphasizes content quality, technical foundations remain essential.
Ensure:
- Mobile first design
- Fast loading speed
- Secure connection
- Clean structured data implementation
Technical weaknesses amplify during core updates. Discover visibility improves when content is supported by an integrated digital marketing strategy that reinforces brand trust and audience engagement.
For example, improving site architecture and crawl efficiency can strengthen overall performance even for streamlined designs such as one page websites.
Is This A Penalty
No.
Core updates are not manual penalties. They are system wide recalibrations.
If traffic declined, it does not mean you violated guidelines. It means the evaluation criteria shifted.
Recovery requires improvement rather than reactive measures such as mass link removal or content deletion without analysis.
What This Update Signals For The Future
The February 2026 Discover Core Update reinforces several long term trends.
- Authenticity matters
- Experience signals matter
- Engagement quality matters
- Authority depth matters
- Low effort automation is risky
Google continues to move toward rewarding content that genuinely satisfies users.
Discover magnifies this because exposure depends heavily on engagement feedback loops.
Websites that align with user first publishing models will adapt more easily to future updates.
Final Thoughts
The Google February 2026 Discover Core Update represents a refinement rather than a disruption. It strengthens existing quality principles instead of introducing entirely new rules.
For publishers and businesses, the path forward is clear.
- Invest in expertise.
- Create meaningful content.
- Improve engagement.
- Build authority gradually.
Discover can generate powerful traffic surges. However, sustainable growth comes from building a trusted content ecosystem that delivers real value.
Discover will continue evolving. The most resilient websites will be those that focus on helping users first, maintaining consistent standards, and adapting thoughtfully to change.
When your strategy centers on helping users rather than chasing algorithms, core updates become opportunities to improve rather than threats to fear.
The February 2026 update serves as a reminder that quality, trust, and depth remain the foundation of lasting visibility.





























